How to operate a drone safely and effectively opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to innovative industrial applications. This guide provides a comprehensive understanding of drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and legal considerations. We’ll explore the essential components of a drone, delve into safe flight practices, and equip you with the knowledge to capture stunning aerial footage.
Whether you’re a novice or seeking to refine your skills, this resource will empower you to confidently take to the skies.
Understanding the nuances of drone flight requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. This guide breaks down the complexities into manageable steps, providing clear explanations and illustrative examples. We’ll examine various drone types, flight modes, and software applications, empowering you to select the optimal tools for your specific needs. By the end, you’ll possess a solid foundation for safe, responsible, and enjoyable drone operation.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various components of a drone and the associated terminology is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the functions of key drone parts and provides a glossary of common terms.
Drone Component Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated operation of several key components. These include:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to lift off, move, and hover. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into rotational motion. Brushless motors are common in modern drones due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, this sophisticated computer processes data from various sensors (gyroscopes, accelerometers, barometers, GPS) to maintain stability and execute flight commands.
- Battery: Provides the power source for all drone components. The flight time is directly related to the battery’s capacity and the drone’s power consumption.
- GPS Module: Enables precise positioning and navigation, crucial for autonomous flight modes and features like Return-to-Home (RTH).
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the speed of each individual motor, allowing for precise control of the drone’s movements.
- Camera and Gimbal: The camera captures photos and videos, while the gimbal (a stabilized mounting system) ensures smooth, shake-free footage.
Drone Terminology Glossary

Familiarizing yourself with common drone terms is essential for understanding manuals, tutorials, and discussions within the drone community.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Altitude Hold | Maintains a constant altitude above ground level. |
| Gimbal | A stabilized mounting system for the camera, reducing vibrations and ensuring smooth footage. |
| Return-to-Home (RTH) | An automated function that guides the drone back to its starting point. |
| Yaw | Rotation of the drone around its vertical axis. |
| Pitch | Movement of the drone forwards or backwards. |
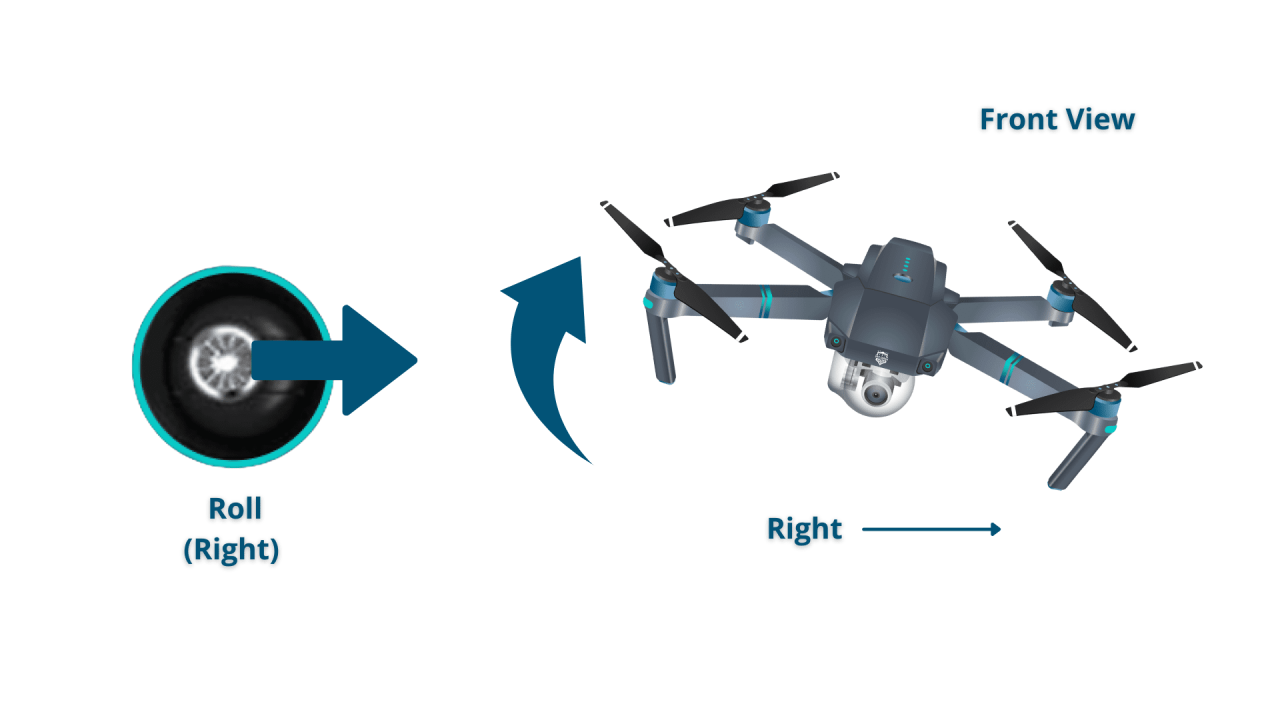
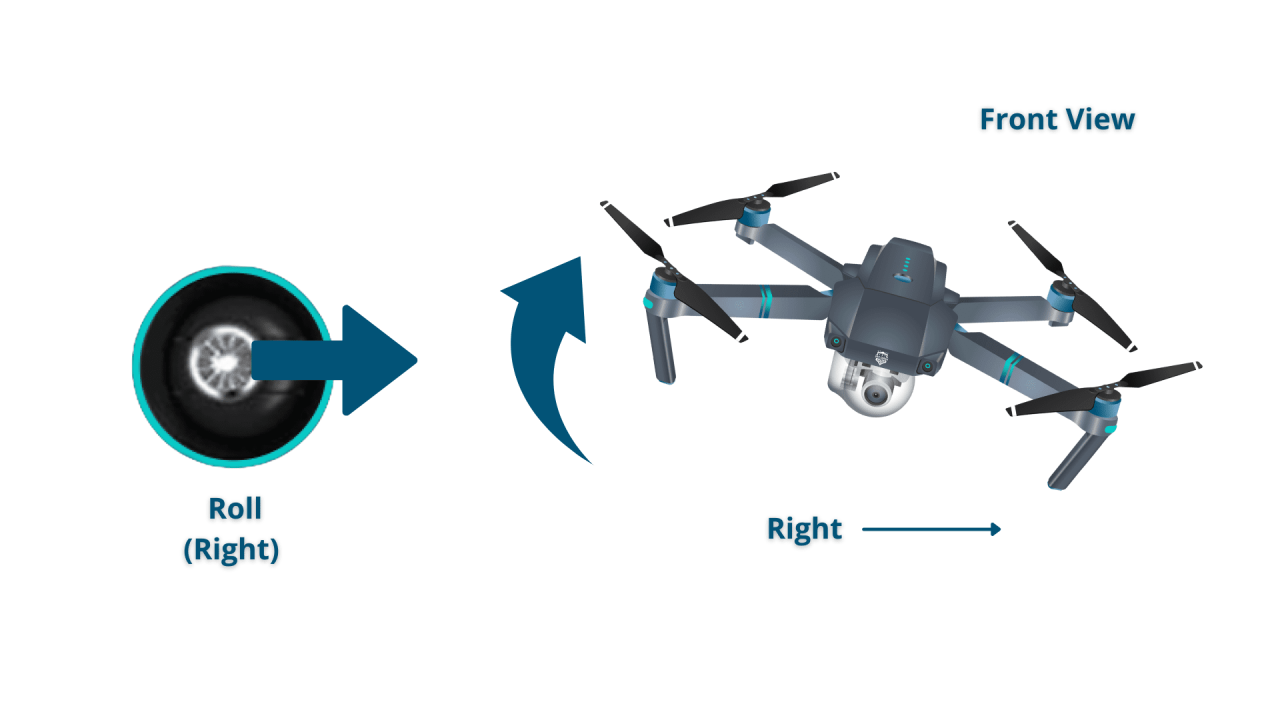
| Roll | Movement of the drone left or right. |
| Throttle | Controls the drone’s ascent and descent. |
| LiPo Battery | Lithium Polymer battery, a common type of rechargeable battery for drones. |
Drone Battery Comparison
Different types of drone batteries offer varying performance characteristics. The choice of battery depends on factors like flight time requirements and payload capacity.
| Battery Type | Voltage (V) | Capacity (mAh) | Approximate Flight Time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo 3S 11.1V 1500mAh | 11.1 | 1500 | 15-20 (varies by drone model) |
| LiPo 4S 14.8V 2200mAh | 14.8 | 2200 | 25-30 (varies by drone model) |
| LiHV 4S 16.8V 2200mAh | 16.8 | 2200 | 25-35 (varies by drone model) |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety procedures are paramount to ensuring a safe and successful drone flight. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents and damage.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety regulations. A crucial step is familiarizing yourself with the flight mechanics, and for a comprehensive guide, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will help you confidently navigate the process of taking to the skies with your new drone, ensuring both safe and successful flights.
Proper operation is key to enjoying this exciting technology responsibly.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, systematically check the following:
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage (propellers, arms, body).
- Verify the battery is fully charged and properly connected.
- Check the GPS signal strength.
- Ensure all propellers are securely attached and spin freely.
- Calibrate the IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) if necessary.
- Review the weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation).
- Check for airspace restrictions and obtain necessary permissions.
- Identify potential hazards in the flight area (obstacles, people, animals).
- Inform others about your flight plan.
Identifying and Avoiding Hazards
Careful hazard assessment is crucial for safe drone operation. Factors to consider include:
- Obstacles: Trees, buildings, power lines, and other structures can pose collision risks.
- Weather: Strong winds, rain, snow, and fog can severely impact drone stability and control.
- Airspace Restrictions: Always check for and comply with local airspace regulations and restrictions.
- People and Property: Maintain a safe distance from people, animals, and property to avoid accidents or damage.
Pre-Flight Inspection Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight inspection process can help ensure that all critical steps are followed.
The flowchart would visually represent the steps listed in the Pre-Flight Checklist above, using standard flowchart symbols (rectangles for processes, diamonds for decisions, etc.). It would start with “Begin Inspection” and end with “Flight Ready/Not Ready”.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. A crucial aspect is learning the controls and understanding the drone’s capabilities, which is comprehensively covered in this excellent guide on how to operate a drone. Properly learning how to operate a drone ensures safe and effective flight operations, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable and productive experience.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic flight controls is essential for safe and controlled drone operation. This section explains the functions of the control sticks and common flight maneuvers.
Flight Control Stick Functions
Most drones use two control sticks: the left stick controls altitude and direction, while the right stick controls pitch and yaw.
- Left Stick (Vertical): Up/Down controls altitude (throttle); Left/Right controls yaw (rotation).
- Right Stick (Horizontal): Forward/Backward controls pitch (forward/backward movement); Left/Right controls roll (sideways movement).
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing
Smooth takeoffs, hovering, and landings are crucial for safe drone operation. Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area.
- Takeoff: Gently push the left stick upwards to initiate ascent. Maintain a steady ascent rate.
- Hovering: Once at the desired altitude, center the left stick to maintain a stable hover.
- Landing: Gently push the left stick downwards to initiate descent. Maintain a slow and controlled descent rate.
Flight Modes
Many drones offer different flight modes to adjust the level of control and stability. Common modes include:
- Beginner Mode: Limits the drone’s speed and responsiveness, ideal for beginners.
- Sport Mode: Allows for faster speeds and more aggressive maneuvers, suitable for experienced pilots.
- GPS Mode: Uses GPS for position hold and return-to-home functionality.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to the pilot, even without GPS.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Advanced flight techniques enable more precise and complex maneuvers. This section explores waypoint navigation, camera stabilization, and emergency procedures.
Precise Maneuvers and Environmental Considerations
Performing precise maneuvers requires practice and a good understanding of drone dynamics. Waypoint navigation allows for pre-programmed flight paths, while camera stabilization ensures smooth, shake-free footage. Flying in urban areas requires extra caution due to increased obstacles and airspace restrictions. Open fields offer more freedom but still require awareness of wind conditions.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. Here’s a step-by-step guide for common scenarios:
- Low Battery: Initiate Return-to-Home (RTH) immediately. If RTH fails, perform a controlled descent.
- Loss of Signal: Most drones have a failsafe mechanism that initiates RTH. If not, attempt to regain signal; otherwise, prepare for an emergency landing.
- Unexpected Malfunction: Attempt to regain control; if unsuccessful, prepare for an emergency landing.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. This section details the process and provides tips for compelling shots.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
The process involves selecting the right camera settings (aperture, shutter speed, ISO), understanding lighting conditions, and utilizing the drone’s flight capabilities to achieve desired perspectives and movement.
Camera Setting Effects, How to operate a drone
Understanding the interplay between aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is crucial for achieving the desired image quality. Aperture controls depth of field, shutter speed controls motion blur, and ISO controls sensitivity to light.
Tips for Composing Aerial Shots
Creating compelling aerial shots involves careful planning and execution. Consider these tips:
- Leading Lines: Utilize roads, rivers, or other features to guide the viewer’s eye.
- Rule of Thirds: Place key elements off-center for a more visually appealing composition.
- Symmetry and Patterns: Capture repeating patterns or symmetrical scenes for visually striking images.
- Perspective: Use altitude and angle to create unique perspectives.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This section Artikels a maintenance schedule and common troubleshooting steps.
Maintenance Schedule

A regular maintenance schedule helps prevent problems and extends the lifespan of your drone. This includes cleaning propellers and the drone body, checking for loose screws or damaged parts, and calibrating sensors as needed.
Common Malfunctions and Causes
Common drone malfunctions include motor problems, GPS errors, and battery issues. Identifying the cause is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting Steps
Troubleshooting involves systematically checking components and settings to identify and resolve issues. This may involve checking battery levels, inspecting motor connections, recalibrating sensors, or updating firmware.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and complying with local regulations. This section discusses legal aspects and ethical considerations.
Regulations Governing Drone Operation
Regulations vary by location and may include licensing requirements, airspace restrictions, and operational limitations. It is crucial to research and comply with all applicable laws and regulations before flying.
Privacy and Unauthorized Surveillance
Respecting privacy is crucial. Avoid flying over private property without permission and refrain from unauthorized surveillance.
Ethical Considerations for Responsible Drone Use
- Obtain necessary permissions before flying in restricted areas.
- Respect the privacy of others.
- Avoid flying near airports or other sensitive areas.
- Fly responsibly and safely, avoiding reckless maneuvers.
- Comply with all applicable laws and regulations.
Drone Software and Apps
Drone control apps and flight planning software significantly enhance drone operation. This section explores their features and functions.
Features and Functions of Popular Drone Apps
Drone apps provide control over various drone functions, including flight modes, camera settings, and GPS navigation. They also offer features like live video feed, flight logs, and firmware updates.
Comparison of Drone Flight Planning Software
Flight planning software allows for pre-programming flight paths, including waypoints, altitude settings, and camera angles. This enhances efficiency and precision, particularly for complex aerial photography or surveying tasks.
Using a Drone App to Set Waypoints and Plan a Flight Path
The process typically involves selecting the desired waypoints on a map within the app, setting parameters like altitude and speed, and then initiating the automated flight sequence. The app will guide the drone along the pre-planned path.
Illustrative Examples of Drone Use
Drones have found applications across various industries. This section showcases examples and discusses their benefits and limitations.
Applications in Different Industries
Drones are utilized in agriculture for crop monitoring and spraying, in construction for site surveys and inspections, and in search and rescue for locating missing persons or assessing disaster areas. Other applications include delivery services, infrastructure inspections, and mapping.
Benefits and Limitations of Drone Use for Specific Tasks
Drones offer advantages like cost-effectiveness, accessibility to difficult-to-reach areas, and enhanced efficiency. However, limitations include battery life, weather dependency, and regulatory restrictions.
Visual Description of a Complex Maneuver
Imagine a drone performing a smooth, controlled 360-degree rotation. The drone maintains a stable altitude and orientation throughout the maneuver, its propellers whirring steadily as it gracefully pivots on its vertical axis. The camera, mounted on a gimbal, smoothly captures the surrounding landscape as it rotates, producing a seamless and captivating aerial view.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a journey of continuous learning and refinement. This guide has equipped you with the foundational knowledge and practical skills necessary for safe and responsible drone piloting. Remember to prioritize safety, adhere to all regulations, and continuously expand your understanding of drone technology and its applications. As you gain experience, you’ll unlock the full potential of aerial perspectives, capturing stunning visuals and contributing to innovative applications across diverse fields.
The sky’s the limit – safely and responsibly, of course.
Commonly Asked Questions
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and autonomous flight modes are ideal for beginners. Look for features like obstacle avoidance and return-to-home functionality.
How often should I calibrate my drone?
Calibration frequency depends on usage, but it’s recommended to recalibrate your drone’s compass and sensors after significant impacts or every few months for optimal performance.
What are the common causes of drone battery failure?
Overcharging, deep discharging, extreme temperatures, and physical damage can all contribute to drone battery failure. Always follow the manufacturer’s charging guidelines and store batteries properly.
How do I handle a drone malfunction mid-flight?
Prioritize safety. If possible, attempt a controlled descent. If loss of control occurs, activate the return-to-home function (if available) or prepare for an emergency landing in a safe location.